Meteosat images
Meteosat images |
Don't hesitate to contact us to receive for free the locations of the centers or corners of the Meteosat (Nadir at 0°,0°) pixels in latitude and longitude in a CSV file.
The path of Meteosat (Nadir at 0°,0°) images, from satellite to rooftop dishes
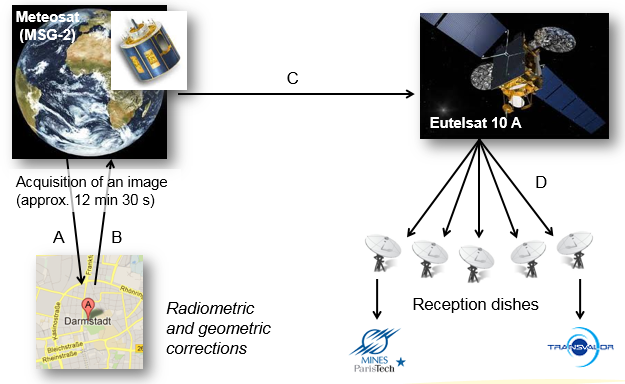
Meteosat images are disseminated every 15 min.
After image collection, the images are sent down to Darmstadt in Germany for geometrical rectifications and radiometric calibration. Images are sent back to Meteosat, and then transmitted to EutelSat's HotBird-6 satellite in GEO located at 13º E longitude for dissemination. The service was initiated at the end of April 2003 utilizing data file distribution via DVB-S (Digital Video Broadcast-Satellite) to a wide audience thanks to reception stations (dishes) located within the geographical coverage zone.
Since early 2011, MINES ParisTech and Transvalor propose a duplicated and synchronized acquisition chain, with two dishes installed on each of their premice rooftops.
Meteosat image (Nadir 0°,0°) characteristics and spatial resolution
The Meteosat satellites are geostationnary, i.e. they operate in equatorial orbits at an altitude of 35 790 kilometers above the surface of Earth. The size of the image is 3712 by 3712 pixels. You need approx. 354 000 pixels to cover the whole Europe, 307 000 for the Arabian Peninsula, 63 000 for Turkey and 48 000 for France. Don't hesitate to contact us to receive for free the locations of the centers and corners of the Meteosat pixels in latitude and longitude in a CSV file. | 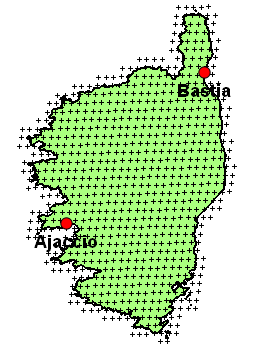 Corners of MSG pixels for Corsica |
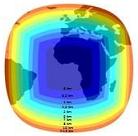
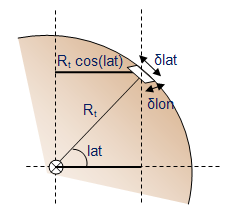
The spatial resolution is the size of the projection a MSG pixel onto the Earth surface. It depends on the latitude and longitude of this projection. For MSG, the spatial resolution is illustrated on the right hand side. The nadir, i.e. the point of the Earth surface located just below the satellite, is (lat, lon) = (0°,0°) and corresponds to the center of the image. The spatial resolution at nadir is 3 km and is decreasing as we moved away from this point. The resolution ranges from 3 km to more than 12 km on the edges of the planet.
| Meteosat spatial resolution. Click on the image to magnify. Copyright MINES ParisTech 2009
Size of a MSG pixel on the Earth surface |
| Sector | Name | Channels | Longitude | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
East Atlantic
| Meteosat Third Generation | 16 channels: 8 between 0.4 µm to 2.1 µm (1 km spatial resolution), and 8 in the thermal spectral domain between 3.8 µm to 13.3 µm (2 km). | 0° |
|
| Meteosat-11 (Operational) | 1 km (for High Resolution Visible) and 3 km (2 visible, 1 Near InfraRed, 6 InfraRed and 2 Water Vapor) | 0° |
| |
| Meteosat-10 | 0° |
| ||
| Meteosat-9 | 9.5° |
| ||
Indian ocean
| Meteosat-8 (Operational from 1 Feb. 2017) | 41.5° |
| |
| Meteosat-7 | 2.5 km (for the channel VIS/HRV) and 5 km (for the IR and the WV channels) | 57.5° |
|